Instructions on labor protection for workers servicing manure removal systems. Occupational safety for remote workers How to conduct an introductory briefing for a remote worker
On labor protection and the procedure for conducting each of them will allow the responsible person to competently convey to the attention of the employees of the enterprise the fundamental points on safety. Employees who want to avoid trouble at work should pay special attention to the rules for being at the workplace, preparing and carrying out work activities.
Why is it important to instruct employees in enterprises?
Starting from kindergarten and school, each child is given health briefings in order to effectively teach safe behavior. The adult population employed in the manufacturing sector gets acquainted with other norms and standards. In accordance with the peculiarities of the process, the workers are informed of the rules for conducting work, the subtleties of the organization, compliance with safety regulations, they are introduced to the rights and obligations.
The main types of briefings for employees
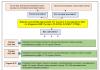
Domestic labor legislation has clearly defined norms confirming the obligation of the employer to conduct briefings on labor protection at the workplace. This also includes the need for professional training of company employees working in conditions that are far from ideal. Familiarization with labor protection requirements can be conditionally divided into two types:
- Primary instruction. It is carried out on the day when the employee starts work or on the first days from the date of performance of official duties.
- Secondary instruction. It implies the presence at the enterprise of a well-functioning system of training in labor protection and the organization of briefings. These staff units should be responsible for the result (a sufficient level of staff awareness) achieved through intelligible and timely setting of tasks.
Who should conduct the briefing at the enterprise?
The management of the enterprise is responsible for informing the personnel. Workplace safety briefings may be delegated to other responsible persons appointed by the directors. It is extremely important that at the end of their conduct, employees can demonstrate high-quality assimilation of the theoretical part of the training material. Employees who evade briefings should be removed from the production process. The wages of these workers are not retained. An employee who has shown unsatisfactory results and low quality of knowledge is sent for retraining.
Differences between briefings for workers
- introductory- are necessary for familiarization by everyone, including those who only plan to find a job or will be present on the territory of the enterprise for a limited time, regardless of profession and rank, seniority and qualifications.
- Primary- their purpose is to inform the employee who is starting to perform professional duties at a new workplace. Of particular importance is the passage of instruction by trainees, students.
- Repeated- relate to the same persons who were instructed when applying for a job. The frequency of technical guidance is on average 6 months.
- unscheduled- relevant in case of receipt of new information on labor protection at the enterprises. Workplace briefings can also be carried out for people who interrupt work for a long time.
- Target- familiarization of an official sent to perform one-time work requiring additional documentation and permits.

Place for staff briefing
There are no specific legal acts regulating the mass procedure for the implementation of programs for instructing labor protection in the workplace. Step-by-step algorithms are developed by each enterprise in accordance with the characteristics of their activities and workflow. But if we take into account the general provisions for instructing, then:
- Induction training prepared by the labor protection department. Often, enterprises do not have such units, and therefore HR inspectors are appointed as responsible persons. Such instruction is carried out in places designed for the number of instructed persons (offices, assembly halls, classrooms).
- Initial briefing on labor protection. At the workplace, instructions are distributed in most cases, but if the manager explains safety standards to a whole group of workers, the premises for team meetings are suitable. Retraining proceeds in a similar way.
- Unscheduled briefing carried out by a specialist in the place that will be best suited for this. In cases where the reason for an unexpected briefing was an accident at work, the technologies of the work process have changed, equipment has been replaced, etc., employees are trained directly at the workplace. If safety clarifications are affected by legislative innovations, any room with sufficient capacity is suitable for group instruction.

Is on-the-job training required?
As for the targeted technical clarification, here one can observe a significant tightening of the order of its organization in the workplace. In this case, the briefing on labor protection is carried out before:
- issuance of an order or permission to perform work;
- the beginning of the implementation of one-time production tasks.
Exceptions are mass events and the process of eliminating the consequences of an accident and natural disasters. So, the choice of a place for instructing the group is carried out in rooms equipped for these purposes, and in the absence of such, one should proceed from the current situation at the discretion of the management.
How often should workers be briefed?
The timing of explanatory activities at the workplace and the frequency of briefings on labor protection are regulated by legislative provisions. They are based on the following rules:
- introductory is carried out at the stage of registration (employment) of the employee;
- primary is carried out immediately before admission to direct professional duties, internship;
- repeated requires regularity, and therefore is carried out at least once every six months;
- targeted and unscheduled briefings are required if necessary.

Safety training sequence
It should be noted that the order of instruction is preserved in the above order. Compliance with the sequence and timing of the briefing by employees indicates the correct organization of the safety system at the enterprise. Thus, primary instructions on labor protection are not carried out before introductory ones, and re-training in safety precautions is not carried out without primary. In cases where a discrepancy in time is found in the journal and summary tables of types of labor protection briefings, the competent control authorities see such a discrepancy as evidence of a formal approach to the safety of workers.
Do I need to coach remote employees?
Some entrepreneurs are concerned about the question of whether there is a need to instruct those employees who, in accordance with an employment contract, perform their official duties remotely (at home) on labor protection. Such employees are popularly called homeworkers. Despite the fact that they work at the place of their actual place of residence, the employer is obliged to provide persons with the necessary equipment, raw materials, and materials. In addition, the manager should make sure that the organization of labor itself does not run counter to the requirements of labor protection.
The rule on the need to train homeworkers at home is contained in Article 311 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. "Homeworkers" do not deprive them of the need to undergo training on labor protection in the appropriate order. At the workplace or at home - it doesn't matter where the employer organizes the meeting and briefing. A remote worker should not have less security knowledge. You can be exempted from the briefing on the same grounds that are suitable for full-time employees working on company premises.

By the way, it is worth paying attention to the possibility of using the help of household members in the process of performing a professional task at home. But we must not forget that officially labor relations began exclusively between the employer and the contractor. In addition, no one deliberately conducts briefings with family members of a remote employee.
Remote operation and labor protection
The category of employees who perform their duties remotely, outside the office and stationary workplaces, deserves special attention. Hiring such specialists in most cases means, rather, not the need to perform a specific production task, but the receipt of professional services of a single or multiple nature. However, in accordance with the Labor Code (Article 312, part three), labor protection briefings affect the use of equipment and means (materials, raw materials) for production. In addition, the use of the labor of remote employees implies the obligation of the employer:
- ensure the procedure for conducting briefings on labor protection and types of investigation of accidents that occurred to employees;
- implement the instructions of the State Supervision Service regarding remote employees;
- accept submissions from control bodies for consideration;
- engage in insurance of hired remote workers against accidents.

How is distance learning done?
Thus, the need for a series of briefings will be necessary in the prevailing number of cases. Acceptable methods of instructing remote workers are electronic transfers of text documents, other files, conferences in Skype, Viber, WhatsApp and others messengers.
As well as conducting briefings on labor protection at the workplace, the instructions of remote and remote employees must be confirmed by receiving response marks on familiarization. If necessary, this moment is prescribed in the employment contract and indicated in the Charter of Internal Regulations and other documentation.
Is it possible to do without briefings at the enterprise?
Taking responsibility, the employer has the right to release "remote" employees from the mandatory training. If subordinates are not exposed to danger, are not involved in the maintenance of equipment, their release from primary and repeated instruction in labor protection will be quite reasonable and legal. Meanwhile, the introductory briefing should go through the entire workforce of the enterprise, including those who are temporarily on its territory (representatives of partner organizations, medical workers, interns, students, relatives of employees, etc.).

However, it is not worth refusing to conduct timely briefing of personnel to the heads of enterprises and structural divisions. We must not forget that a well-conducted briefing is an affordable and effective measure that allows employees to perform their work duties with maximum dedication without risking their own health and safety.
This instruction on labor protection has been developed specifically for office workers.
1. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS FOR LABOR PROTECTION
1.1. An office worker is allowed to work independently after passing:
- medical examination;
— introductory briefing on labor protection;
– training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements;
- testing knowledge of electrical safety rules with the assignment of the necessary qualification group of admission;
— introductory fire safety briefing;
- checking knowledge of this manual.
1.2. The employee is obliged to fulfill official duties, work on the instructions of his supervisor, comply with the internal labor regulations, comply with labor protection requirements, and take care of property.
1.3. The employee must:
- know the dangerous and harmful production factors that manifest themselves in his workplace;
- know and be able to apply precautionary measures and means of protection (including individual ones) from dangerous and harmful production factors;
- know the operating instructions for the equipment used, office equipment;
- know the connection points of current collectors, switching devices, as well as be able to determine their good condition and be able to turn them off in emergency situations;
- know the ways of personnel evacuation and actions in case of emergencies;
- know the location of fire extinguishing equipment and be able to use them;
- know and be able to provide first aid to the victims;
- follow the rules of personal hygiene;
- use in work only for its intended purpose and only serviceable furniture, fixtures, office equipment and other workplace equipment;
- do not allow the presence of foreign objects in your workplace that interfere with work.
1.4. Depending on the working conditions, various hazardous and harmful production factors may appear in the workplace.
1.4.1. During the operation of a personal computer, the employee may be affected by the following hazardous production factors:
- electromagnetic radiation;
- increased brightness of the light image;
- voltage in the electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body;
- eye strain, attention, prolonged static loads.
1.4.2. During the operation of electrical equipment, a dangerous production factor is electric current. The maximum permissible value of alternating current is 0.3 mA. With an increase in current to 0.6-1.6 mA, a person begins to feel its effect.
Types of electric shock:
- electric shock (paralysis of the heart and breathing);
- thermal burn (electric burn);
— technical damage;
- electrophthalmia (inflammation of the eyes due to the action of an electric current).
1.4.3. Also, the following dangerous and harmful production factors can affect the employee:
- neuropsychic and emotional overload;
- falling objects from a height (from cabinets, shelves);
- rough or sharp surface of equipment, tools, office equipment;
1.4.4. Information about hazardous and harmful production factors arising from the operation of other equipment is contained in the instructions for their operation.
1.5. Employee protection means are:
- protective insulation of wires and cables, current-carrying parts of equipment and parts of equipment that may be energized.
To work on personal electronic computers (hereinafter referred to as PCs), it is recommended to use special spectral glasses.
1.6. For violation of the requirements of this instruction relating to the work performed by him, the employee is liable in accordance with the current labor, criminal and administrative laws of the Russian Federation.
2. HEALTH REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
2.1. Each employee before starting work must:
- remove from the workplace foreign objects and objects that are not required to perform the current work (boxes, bags, folders, books, etc.);
- make sure by external inspection that there are no mechanical damages to the power cords and housings of office equipment, as well as that there are no mechanical damages to electrical wiring and other cables, electrical sockets, electrical switches, lamps, air conditioners and other equipment;
- check whether the furniture is in good condition and conveniently located, whether the equipment of the workplace and the materials necessary for work are conveniently placed on the desktop, whether the approaches to workplaces are free;
- in case of detection of damage and malfunctions of the PC, peripheral devices, office equipment, furniture, fixtures, electrical wiring and other cables, electrical sockets, electrical switches, lamps, air conditioners and other equipment, do not turn on the equipment, do not start work, call technical personnel and report this to your immediate supervisor;
- check if the workplace is adequately lit. In case of insufficient illumination, it is necessary to organize local lighting, and arrange local lighting fixtures so that when performing work, the light source does not blind the eyes of both the worker and those around him;
2.2. Make sure that the work is carried out safely, only after that you can start working.
3. HEALTH REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
3.1. Every employee must:
- keep the workplace in order and cleanliness, avoid cluttering it with documents;
- keep free passages to workplaces, do not clutter up the equipment with objects that reduce the heat transfer of office equipment and other equipment;
- monitor the serviceability of office equipment and other equipment, follow the rules for their operation and labor protection instructions for the relevant types of work;
- in case of a long absence from the workplace, disconnect office equipment and other equipment from the mains, with the exception of equipment designated for round-the-clock operation (network servers, etc.);
- be attentive, not distracted and not distract others;
— in the event of a paper sheet (tape) jam in the output devices, before removing the sheet (tape), stop the process and disconnect the device from the mains, call technical staff or inform your immediate supervisor about this;
- disconnect office equipment and other equipment from the mains, only holding on to the plug of the plug connector;
- do not allow pulling, twisting, bending and pinching equipment power cords, wires and cables, do not allow any objects to be placed on them and come into contact with heated surfaces;
- during the established breaks in work, perform the recommended exercises for the eyes, hands;
- prevent moisture from entering the surface of the PC, peripheral devices and other equipment. Do not wipe with a damp or wet cloth equipment that is under electrical voltage.
3.2. During work it is not allowed:
- touch moving parts of office equipment and other equipment;
— to work at insufficient illumination of a workplace;
- touch the elements of office equipment and other equipment with wet hands;
— switch interface cables, open cases of office equipment and other equipment and independently repair them.
4. REQUIREMENTS FOR LABOR PROTECTION IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS
4.1. In the event of an emergency, an employee must:
- immediately stop work, disconnect office equipment and other electrical equipment from the power grid and report the occurrence of an emergency and its nature to the immediate supervisor, and in his absence to the senior manager; if necessary, leave the danger zone;
- under the guidance of the immediate supervisor, take part in the liquidation of the emergency situation, if this does not pose a threat to the health or life of workers;
- in case of malfunctions in the operation of office equipment or other equipment, as well as in the event of a malfunction in the electrical network (the smell of burning, extraneous noise during the operation of office equipment and other equipment, or the feeling of an electric current when touching their cases, flashing lamps, etc.); e.) disconnect office equipment and other equipment from the mains, call technical personnel and inform your immediate supervisor about this;
- in case of detection of malfunctions of furniture and fixtures, stop using them, call technical staff and inform your immediate supervisor about this;
- in the event of a temporary interruption in the supply of electricity, disconnect office equipment and other electrical equipment from the mains;
- do not start work until the damage and malfunctions of office equipment and workplace equipment are completely eliminated or the emergency situation is eliminated;
- in the event of a fire, it is necessary to stop work, call the fire brigade, disconnect office equipment and other equipment from the mains, notify nearby people about the fire, take measures to evacuate people from the danger zone and take part in extinguishing the fire with the available primary fire extinguishing equipment, and if it is impossible eliminate the fire and leave the danger zone, acting in accordance with the instructions for fire safety and evacuation plans;
- extinguish the fire with the help of powder or carbon dioxide fire extinguishers with the obligatory use of personal protective equipment;
- in case of accidents with other employees, provide the victim with first aid, help deliver him to a health center or the nearest medical facility, and, if necessary, call medical workers to the scene of the incident;
- immediately inform your immediate supervisor about the accident that happened to the employee or through his fault, as well as about any accident involving other employees of his or a third-party organization, witnessed by the employee;
- take measures to preserve the situation of the accident, if this is not associated with a danger to the life and health of people;
- when investigating an accident, the employee must report all the circumstances of the incident known to him;
- when committing terrorist acts or the threat of committing them, act in accordance with the recommendations for safety in emergency situations in force in the organization;
- in case of detection in the office premises of violations of labor safety requirements that cannot be eliminated on their own, as well as in the event of a threat to the life or health of the employee or other employees, inform their immediate supervisor about this, suspend work and leave the danger zone.
5. REQUIREMENTS FOR HEALTH AND SAFETY AFTER THE END OF WORK
5.1. After finishing work, you must:
- disconnect office equipment and other equipment from the mains, with the exception of equipment that is defined for round-the-clock operation (fax, network servers, etc.);
- tidy up the workplace, paying special attention to its fire-fighting condition;
- close the windows;
- turn off the lights;
- inform your immediate supervisor of all shortcomings discovered during work.
Question from Konstantin
Good afternoon Colleagues, a question about remote employees. What to do with them? To train on labor protection - not to train? To instruct is not to instruct. According to Art. 312.3 "... training in safe methods and techniques for performing work ..., briefing on labor protection, internships and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements" they are not required, but they must be familiarized with the requirements of labor protection! The same question arises for fire safety and electrical safety briefings. Maybe someone faced a similar situation. Remote employees are scattered almost throughout the European part of the Russian Federation. Thanks in advance.

Reply to Konstantin
Greetings Konstantin!
"Labor Code of the Russian Federation" dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (as amended on April 2, 2014, as amended on June 4, 2014) (as amended and supplemented, effective from April 13, 2014)
Article 312.3. Features of the organization and labor protection of remote workers
The procedure and terms for providing remote workers with the equipment, software and hardware, information security tools and other means necessary for the performance of their duties under an employment contract on remote work, the procedure and terms for submitting reports on the work performed by remote workers, the amount, procedure and terms for paying compensation for the use by remote workers of equipment belonging to them or rented by them, software and hardware, means of protecting information and other means, the procedure for reimbursement of other expenses related to the performance of remote work is determined by the employment contract on remote work.
In order to ensure safe conditions and labor protection for remote workers, the employer fulfills the obligations provided for in paragraphs seventeen, twentieth and twenty-one of the second part of Article 212 (see below) of this Code, and also familiarizes remote workers with the requirements of labor protection when working with equipment and means recommended or provided by the employer. Other obligations of the employer to ensure safe conditions and labor protection, established by this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, do not apply to remote workers, unless otherwise provided by an employment contract on remote work.
Article 212. Obligations of the employer to ensure safe conditions and labor protection
The employer must ensure:
— investigation and accounting, in accordance with the procedure established by this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, of accidents at work and occupational diseases; (As amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ dated June 30, 2006)
- fulfillment of instructions of officials of the federal executive body authorized to exercise federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, other federal executive bodies exercising state control (supervision) in the established field of activity, and consideration submissions of public control bodies within the time limits established by this Code and other federal laws; (as amended by Federal Laws No. 122-FZ of 22.08.2004, No. 90-FZ of 30.06.2006, No. 242-FZ of 18.07.2011)
- Compulsory social insurance of employees against industrial accidents and occupational diseases ...
Answer to the question:
For remote workers, introductory and primary briefings on labor protection are carried out.
Don't miss: the main article of the month from leading specialists of the Ministry of Labor and Rostrud
Encyclopedia of labor protection "turnkey" with a unique set of mandatory samples from the Kadra System.
For all persons entering work, as well as for employees transferred to another job, the employer or a person authorized by him is obliged to instruct on labor protection, organize training in safe methods and techniques for performing work and providing first aid to victims (part two of article 225 of the Labor Code RF). This general requirement applies to all employees, including remote employees, but for this category of workers there are specifics for carrying out labor protection measures (part two of article 312.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The most important changes of this spring!
-
There have been important changes in the work of personnel officers that should be taken into account in 2019. Check in the game format whether you have taken into account all the innovations. Solve all the tasks and get a useful gift from the editors of the Kadrovoe Delo magazine. -
Read the article: Why should a personnel officer check accounting, is it necessary to submit new reports in January and what code to approve for a time sheet in 2019 -
The editors of the Kadrovoe Delo magazine found out which habits of personnel officers take a lot of time, but are almost useless. And some of them may even cause bewilderment in the GIT inspector. -
Inspectors of the GIT and Roskomnadzor told us what documents should never be required from newcomers when applying for a job. You probably have some papers from this list. We have compiled a complete list and selected a safe replacement for each prohibited document. -
If you pay vacation pay a day later than the deadline, the company will be fined 50,000 rubles. Reduce the notice period for the reduction by at least a day - the court will reinstate the employee at work. We have studied court practice and prepared safe recommendations for you.
1.2. Violation by an employee of labor protection requirements at the workplace can lead to an accident: mechanical injury from fragments of the tool used, moving parts of the machine and seizure of parts of clothing, as well as electric shock.
1.3. It is necessary to ensure that metal cutting processes and used metalworking devices comply with safety requirements in accordance with current state standards.
1.4. The mechanical workshop must be equipped with personal protective equipment and fire extinguishing equipment.
1.5. Stationary metalworking machines must be installed on solid foundations or bases, carefully aligned, firmly fixed, painted. Passages, driveways, hatches of wells in the workshop should be kept free and not cluttered with materials, blanks, parts, waste and containers. Installation of machines on hatches of wells is not allowed.
1.6. Persons at least 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, training, instruction and testing of knowledge on labor protection are allowed to work on metalworking machines. The machine operator must have an electrical safety group II and a certificate confirming the right to work on this type of machine.
1.7. Installation and removal from metalworking machines of devices, parts, fixtures and tools weighing more than 16 kg is carried out using lifting mechanisms.
1.8. The installation of abrasive tools on metalworking machines is carried out only by workers who know the rules and have practical skills in inspecting and installing abrasive tools. These workers are trained in the rules and regulations for working with abrasive tools.
1.9. All employees are provided with overalls and personal protective equipment in accordance with applicable regulations.
1.10. Lighting of metalworking machines (general and local) should provide a clear visibility of the process of processing products, divisions on control and measuring tools, feed dials, as well as tables of machine settings and controls. For local lighting, a voltage of no higher than 12 V should be used.
1.11. Metalworking machines that process dust-forming materials (cast iron, bronze, etc.) must be equipped with devices for removing this dust during operation (local suction).
Machine tools working with oil, kerosene, etc. cooling in the presence of abundant vapor emission are equipped with exhaust ventilation.
1.12. All machines, machine tools and installations that generate noise during operation of more than 70 dBa must be equipped with devices to eliminate it or reduce it as much as possible.
2. HEALTH REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
2.1. Put on overalls, tuck your hair under a headgear and make sure that the condition of the overalls excludes the possibility of its capture by moving parts of a metalworking machine or tool.
2.2. In order to prevent skin diseases of the hands when using cooling oils and liquids on metalworking machines, lubricate hands with prophylactic pastes and ointments before starting work.
2.3. Inspect the workplace, remove from under your feet everything that can interfere with work, clear the aisles and not clutter them up, check the condition of the wooden grate under your feet.
2.4. Check the serviceability of personal protective equipment, protective screens, tools, fixtures for fixing parts.
When checking the abrasive wheel, it is necessary to carefully examine it in order to detect cracks or other defects. When tapped with a wooden mallet, the whole abrasive wheel should produce a clear sound.
At the cutting tool, check the absence of cracks, breaks, the strength of fastening of hard alloy plates, etc.
2.5. Check the serviceability and reliability of the devices for fastening the tool and the correctness of its fastening, while taking into account the following requirements:
The flanges for fixing the abrasive wheel must have the same diameter on both sides of the wheel. Between the flanges and the circle, gaskets made of cardboard, rubber, leather should be placed, overlapping the surface of the flanges by at least 1 mm around the entire circumference;
Drill chucks must not have protruding parts. When fixing a part in a chuck or faceplate of a lathe, grab the part with cams as far as possible. Do not use clamping devices with worn jaw working planes;
When installing the cutting tool on the milling machine, check the cleanliness of the spindle taper hole and the surface of the mandrel or cutter.
2.6. Check and ensure sufficient lubrication of the metalworking machine; when lubricating, use only appropriate tools.
2.7. Check the presence, serviceability and strength of fastening:
Guards and safety covers of gear wheels, drive belts, rollers, protruding parts of the bar, etc.;
Current-carrying parts of electrical equipment (starters, knife switches, transformers);
Safety devices for protection against chips and splashes of cooling oils and liquids.
2.8. Visually check the serviceability of the grounding of the metal parts of the metalworking machine and equipment (bed, motor housings, metal casings of starting devices).
2.9. Check the idle speed of the metalworking machine:
Serviceability of control mechanisms (button devices and brakes);
Serviceability of fixation of levers of inclusion and switching;
No jamming, vibration, beating of the moving parts of the machine.
2.10. In the event of a malfunction of the machine, fixtures, tools or personal protective equipment, the master should be informed about this.
It is not allowed to work on a faulty and unguarded machine, as well as the use of faulty or worn tools.
3. HEALTH REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
3.1. The workplace should be kept clean, under the feet of the worker it is necessary to ensure that there is no oil, coolant, chips, scraps, etc.
3.2. To collect cooling and lubricating liquids and prevent them from spilling on the floor, metalworking machines must be equipped with appropriate collections (pallets, troughs, etc.).
3.3. At the workplace, under the feet of the worker, a serviceable wooden grating should be installed with a distance between the planks of 25 - 30 mm.
3.4. When working on a lathe:
When processing long parts, use special supporting devices (lunettes);
Install (screw on) and remove (screw) the chuck (faceplate) from the spindle only with manual rotation. It is not allowed to screw the chuck (faceplate) by braking;
When centering parts on the machine, cleaning, grinding parts with an emery cloth, filing, scraping, measuring parts, changing the cartridge and parts, take the cutting head to a safe distance.
3.5. When milling through windows, slots, keyholes, etc. the cutter should be periodically retracted to eliminate the pressure arising on it and breakage; it is especially necessary to retract the cutter at the end of the pass.
3.6. Do not stop the metalworking machine until the cutting tool has completely exited the workpiece.
3.7. When working on a drilling machine:
When manually feeding, it is forbidden to let go of the drill feed handle;
To avoid breakage of the drill, do not press hard on it. In addition, when the drill is sharply fed, a part or cutting tool can be torn out, which can lead to injury to the worker or others;
When the drill leaves the workpiece, it is necessary to reduce its feed.
3.8. When working on a machine with an abrasive tool:
Ensure that the gap between the handpiece and the working surface of the wheel is less than half the thickness of the part to be ground, but not more than 3 mm;
The shifting of the handrest should be done only when the machine is stopped. After each rearrangement, the handpiece must be securely fixed;
Start work only when the full number of revolutions of the circle is reached.
It is not allowed to work with the side (end) surfaces of the circle, if the circle is not specifically designed for this type of work.
3.9. Wetting the cutting tool with coolants should be done only with a brush.
3.10. During the operation of the metalworking machine is not allowed:
Touching the rotating parts and putting the hand into the zone of their movement;
Application for cooling wetted rags;
Lean on the machine;
Put parts and tools on the machine;
Install a tool or correct the installation of a part on the machine;
Transfer any items through the machine;
Take measurements of the workpiece and manually control the quality of its processing;
Clean, repair, clean and lubricate the machine;
Remove and put on belts on pulleys;
Tighten bolts, nuts and other connecting parts of the machine;
Remove guards from the machine or keep them open.
3.11. It is not allowed to work on metalworking machines in mittens, as well as with bandaged fingers without rubber fingertips.
3.12. Cleaning of chips from metalworking machines should be carried out in a timely manner and mechanized as much as possible.
3.13. To remove chips from a metalworking machine, use appropriate tools (hooks, brushes, etc.). It is not allowed to remove the chips with your hands, blow them off. Remove chips from drilled holes only after stopping the machine tool.
3.14. Do not use compressed air to blow workpieces, products, equipment and clothing.
3.15. If it is impossible to provide metalworking machines with special screens to protect the worker from chips or abrasive dust during work, goggles or protective shields made of transparent material should be used.
3.16. It is not allowed to leave a working metalworking machine unattended. When the worker leaves, the tool should be taken away from the workpiece, the machine should be turned off.
3.17. When repairing, cleaning and lubricating a metalworking machine, a poster should be posted at the starting devices: "Do not turn on - repair."
3.18. When stacking products in stacks at the workplace, the height of the stack is determined from the conditions of its stability and the convenience of removing parts from it. The height of the stack should not exceed 0.5 m for small parts, 1.0 m for medium parts, and 1.5 m for large parts.